Exploring the World of 3D Printing: A Tutorial
Welcome to the fascinating world of 3D printing, where imagination meets reality! In this tutorial, we will delve into the basics of this groundbreaking technology, explaining everything from what 3D printing is to its practical applications, as well as the different types of printers and materials used. So, let’s dive in!
What is 3D Printing?
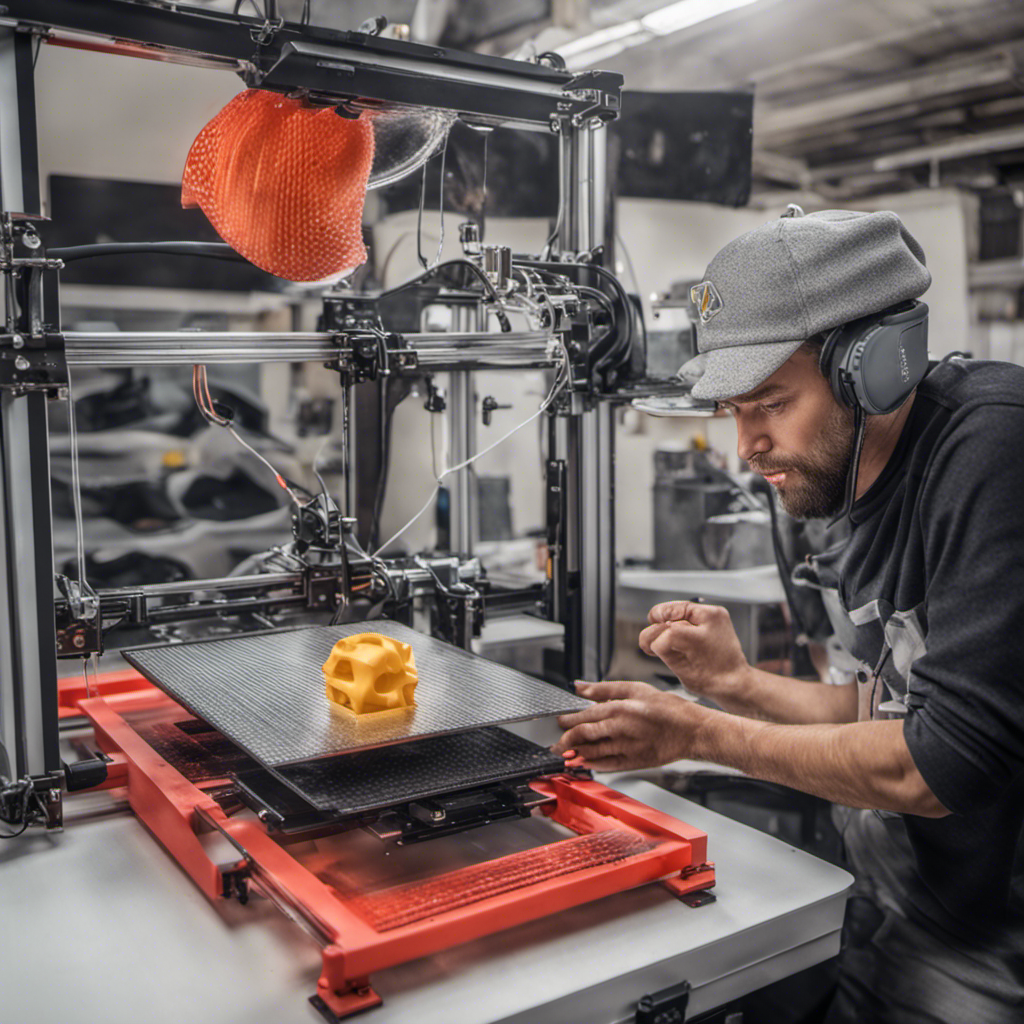
At its core, 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is the process of creating three-dimensional objects layer by layer, based on a digital model or blueprint. Instead of subtracting material (like traditional manufacturing methods), 3D printing builds objects by depositing or solidifying materials, typically in the form of filaments or resins.
A Brief History of 3D Printing
The concept of 3D printing was first introduced in the 1980s, but it wasn’t until the early 2000s that the technology became more accessible and affordable. Since then, it has rapidly evolved, revolutionizing prototyping, manufacturing, and even medical applications.
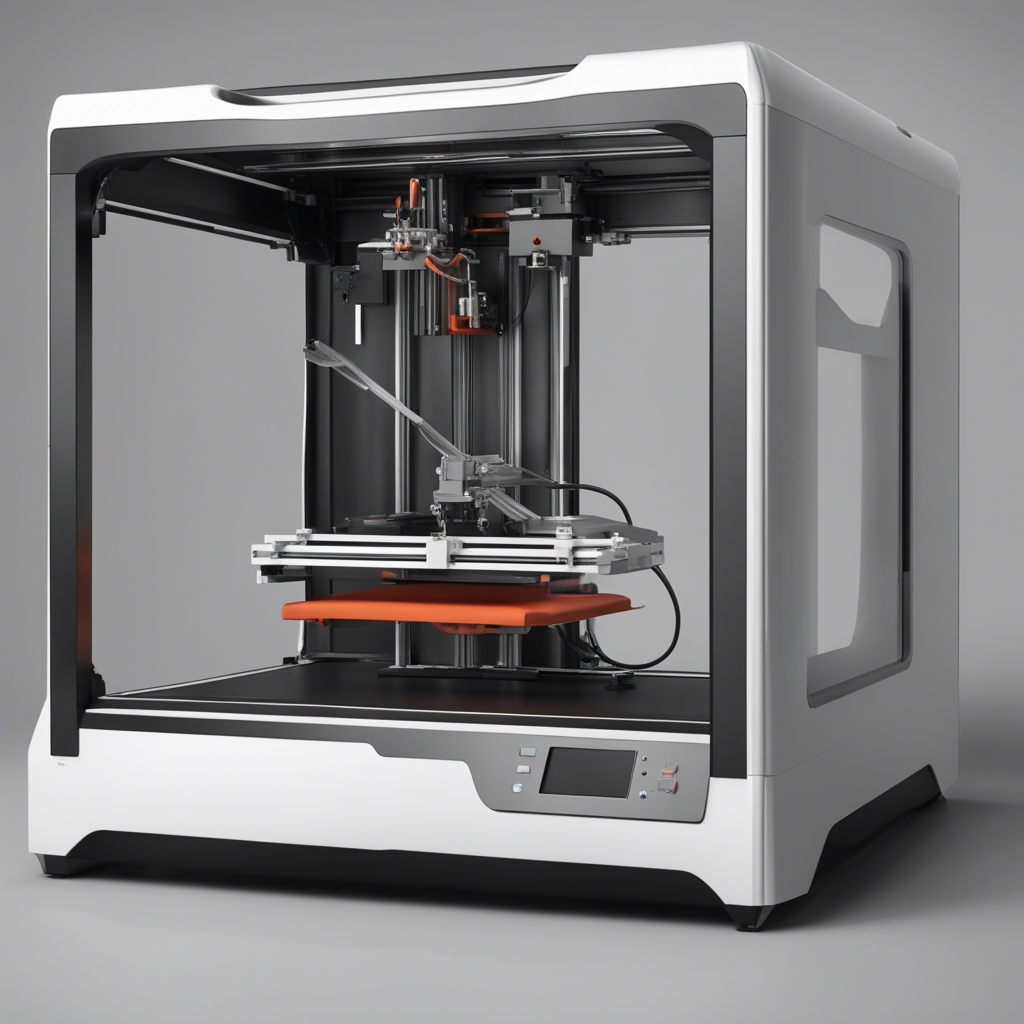
Types of 3D Printers
There are several types of 3D printers available today, each with its own unique advantages and applications. Let’s explore the most common ones:
-
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM printers use thermoplastic filaments, such as ABS or PLA, which are heated and extruded through a nozzle. The filament is deposited layer by layer to create the final object.
-
Stereolithography (SLA): SLA printers utilize liquid resin that is selectively cured by light to create each layer. This technology enables highly intricate designs with smooth surfaces.
-
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS printers employ a laser to selectively fuse powdered materials, such as nylon or metal, layer by layer. This method is ideal for producing functional and durable parts.
Materials Used in 3D Printing
An incredible variety of materials can be used in 3D printing, each offering different properties and applications:
-
Polylactic Acid (PLA): PLA is a biodegradable and easy-to-print filament, making it a popular choice for beginners. It’s commonly used for prototyping, decorative objects, and food-safe applications.
-
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): ABS is a durable and impact-resistant filament that is suitable for functional parts. It requires a heated build platform and proper ventilation due to its fumes.
-
Nylon: Nylon filaments offer high strength, flexibility, and durability. They are often used in industrial applications and for creating functional prototypes.
-
Resin: Various types of resins are available for SLA printers, including standard, flexible, and castable resin. They offer smooth and detailed prints with excellent detail reproduction.
-
Metal: Advanced 3D printers can use powdered metals, such as stainless steel, titanium, or aluminum, to produce strong and precise metal parts.
Applications of 3D Printing
The versatility of 3D printing has led to its adoption in numerous industries and sectors, including:
-
Prototyping: 3D printing allows for rapid and cost-effective prototyping, enabling designers and engineers to quickly iterate and test new ideas.
-
Manufacturing: In some cases, 3D printing is replacing traditional manufacturing methods, as it offers greater design freedom and customization while streamlining supply chains.
-
Medical and Healthcare: 3D printing has revolutionized the medical field, allowing for the creation of patient-specific implants, prosthetics, surgical guides, and even organ and tissue scaffolding.
-
Aerospace and Automotive: The aerospace and automotive industries leverage 3D printing for lightweight parts, complex geometries, and reduced assembly time.
-
Education and Research: 3D printing is being increasingly used in educational institutions to enhance STEM education and promote creativity. It also plays a crucial role in scientific research, enabling the production of specialized equipment or models.
Getting Started with 3D Printing
If you’re eager to get started with 3D printing, here are some steps to help guide you:
-
Choose the Right Printer: Consider your budget, desired features, and intended use to select the best 3D printer. Research reputable companies and read user reviews to ensure quality and reliability.
-
Create or Download a 3D Model: If you are skilled in 3D design, you can create your own model using design software like Autodesk Fusion 360 or SketchUp. Alternatively, you can download pre-made models from online repositories like Thingiverse or GrabCAD.
-
Prepare the Model: Use slicing software, such as Ultimaker Cura or PrusaSlicer, to prepare your 3D model for printing. Adjust settings like layer height, infill density, and support structures for optimal results.
-
Print and Post-Processing: Load the filament or resin into the printer, initiate the print, and monitor the progress. Once the printing is complete, remove any support structures, sand rough edges, and apply finishing techniques as needed.
Conclusion
The world of 3D printing offers a vast array of possibilities and applications. From creating prototypes to revolutionizing industries, this technology continues to reshape our world. By understanding the different types of printers, materials, and applications, you can embark on your own 3D printing journey. As you explore this exciting realm, remember to continue learning, experimenting, and pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
References: